β-glucan in oat is a kind of non-starch polysaccharide existing in the cell wall of endosperm and aleurone layer of oat. β-glucan has good physical properties such as thickening, stability, emulsification and gelation. It is widely used in food, health products and skin care products.
β-glucan is a kind of polysaccharide widely found in microorganisms, mushrooms and plants. It is one of the structural macromolecules that make up the cell walls of higher plants, yeasts and fungi. It has physiological functions such as reducing blood lipids, regulating blood sugar, enhancing immunity and so on. At present, it is generally believed that β-glucan has four functions: clearing intestines, lowering cholesterol, regulating blood sugar and improving immunity.
High viscosity, strong thickening, low GI value, strong sense of satiety; can slow down the absorption of energy materials.
Intestinal fermentation: conducive to fecal excretion, probiotics, balance intestinal ecological stability.
The source of oat β-glucan
The main water-soluble dietary fiber in wheat bran is gathered in the outermost layer of cereals (wheat bran), and oat bran contains 50% more than other parts of oats; β-
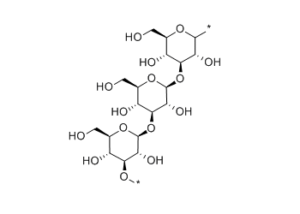
glucan is soluble in water, oat β-glucan molecules have strong water absorption, and have viscosity after dissolving water. Adsorptive.
The role of oat β-glucan: EU-recognized oat β-glucan benefits.
3-4 grams of oat β-glucan a day can lower cholesterol, control blood sugar, gastrointestinal health and satiety.
Evaluation of the European Food Safety Agency:
Regular consumption of oats and barley β-glucan helps maintain normal blood cholesterol concentrations; oat β-glucan has been shown to lower blood cholesterol; eating barley or oat β-glucan helps reduce postprandial blood sugar; oat grain fiber helps to increase fecal volume.
How does oat β-glucan lower cholesterol?
Oat β-glucan is released when digested in the oat gluten: it forms a high viscosity environment in the digestive tract, binds cholesterol in the intestine, hinders the absorption of cholesterol in the intestine, binds with bile acid in the small intestine, increases the excretion and synthesis of bile acid, accelerates the conversion of cholesterol to bile acid, produces short-chain fatty acids through microbial fermentation in the colon, and inhibits cholesterol synthesis.
Effect of oat β-glucan on blood glucose: only grain-derived β-glucan can reduce the risk of diabetes.
The higher the molecular weight and viscosity of oat β-glucan, the more significant the effect of reducing postprandial glycemic index and insulin level.
Oat β-glucan helps improve intestinal health.
As a kind of soluble dietary fiber, β-glucan can not be digested and degraded, and its viscosity increases after entering the intestine. it interacts with intestinal flora, promotes the growth of beneficial bacteria, always propagates harmful bacteria, improves the structure and diversity of intestinal flora, and stimulates intestinal peristalsis. accelerate the excretion of harmful substances out of the body and improve intestinal health.
In addition, studies have shown that oat β-glucan can improve immunity.
Who needs oat beta-glucan more?
Those who require a low-sterol diet; those who need to control blood sugar, those with poor defecation, those with dysfunctional intestinal flora, and people who lose weight.






Leave A Comment